Annuity Calculator Present Value Formula – The present value of the increasing annuity calculator is used to calculate the value of the increasing amount at the rate g received at the end of each period, taking into account the ‘discount rate i’, for the period today.
The profitability index (PI) of a series of cash flows is found by computing the present value of all cash flows from a project (PV) and dividing the value by the initial investment (I). The profitability index is sometimes called the value investment ratio.
Annuity Calculator Present Value Formula
The concept of the present value of a lump sum is the starting point for many time value of money calculations, including the present value of an annuity, and the net present value calculation.
Annuity Vs Perpetuity
The present value of an increasing perpetuity formula is used to calculate the present value of a series of periodic payments that increase at a constant rate each period. Payments made at the end of each period continue forever, and a discount rate of i% applies.
The present value of an annuity formula is used to calculate the present value of a series of periodic payments. Payments are for the same amount, made at the end of each period, and a discount rate of i% applies.
The present value of a lump sum formula is used to calculate what the value of cash received in the future is.
The present value of a perpetual formula shows the value of an infinite stream of equal cash flows (PMT) made at regular intervals over time when a discount rate of i% is applied.
Future Value Of Annuities
The present value of an increasing annuity payable formula is used to calculate the present value of a series of periodic payments that increase at a constant rate each period. Payments made at the beginning of each period, and a discount rate of i% applies.
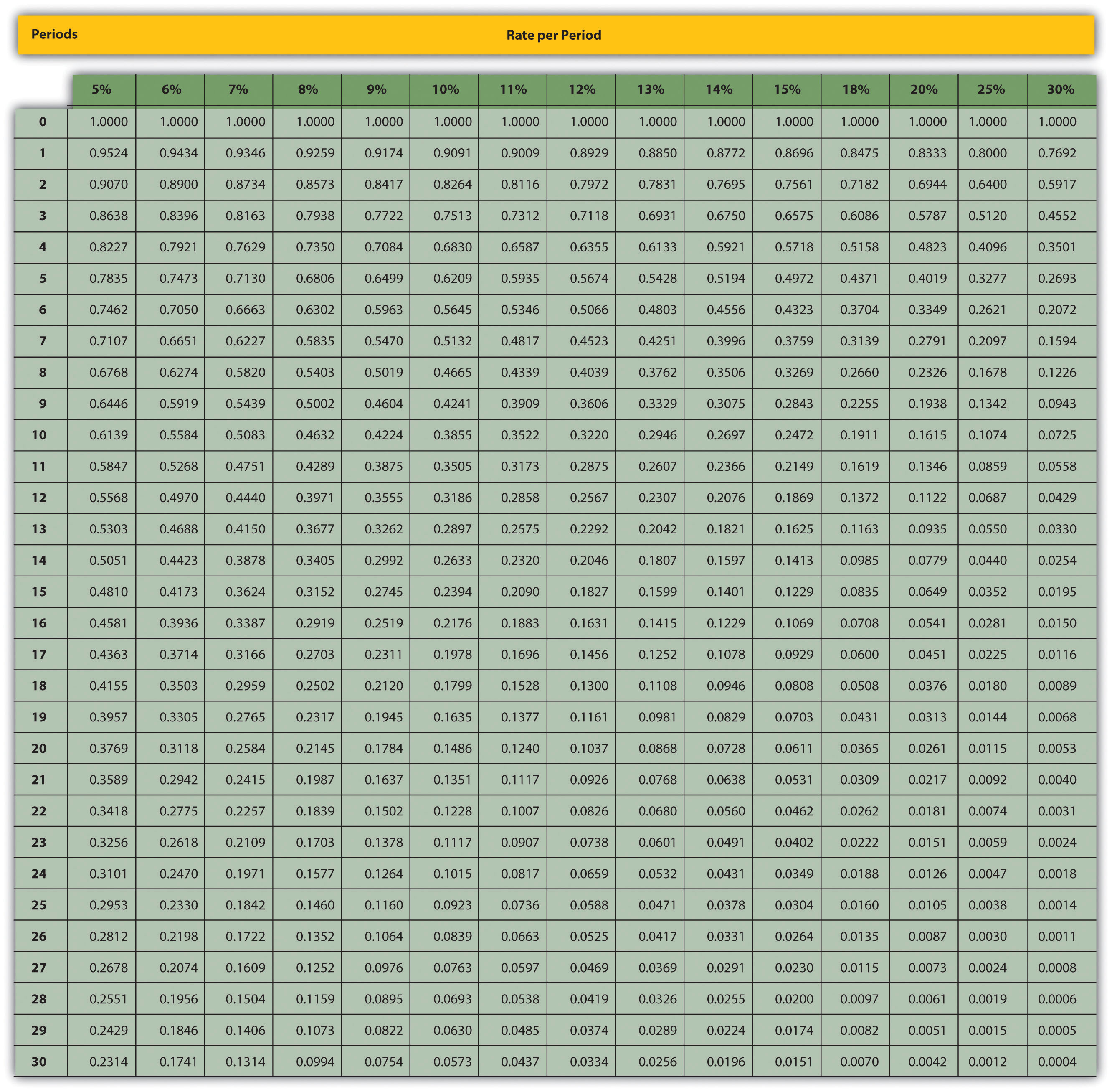
Present value annuity payable tables can be used to calculate annuity payable without the use of a financial calculator.
The tables give a value of 1 obtained at the beginning of each period for n periods with a discount rate of i%.

Present value annuity tables can be used to perform annuity calculations without the use of a financial calculator.
Present Value Vs Future Value
The tables give a value of 1 obtained at the end of each period for n periods with a discount rate of i%.
The concept of time value of money is used in financial management to compare lump sum cash flows that are received or paid at different times.
Lump sum present and future value formulas can be used to calculate the effect of time and compound interest rates on the value of a lump sum. He is best regarded as an example.
The net present value (NPV) of a series of cash flows is found by computing the present value of each cash flow at the appropriate discount rate and then adding them together.
Present And Future Value Of An Annuity
Net present value is used to compare projects and evaluate whether a project is worthwhile. It assumes that a project involves a series of cash flows in or out of the business over a number of years. Have you ever noticed that the prices of expensive products are not advertised? Instead, the companies marketing these high-ticket products promote annuity payment amounts, not the actual sticker price. In fact, a lens is usually needed to ascertain the actual price of these products in advertisements. For example, a Mitsubishi Outlander was recently advertised for only $193 bi-weekly. It doesn’t sound so bad, and you might be tempted to go to a car dealership to buy one of those vehicles. However, the fine print indicates that you need to pay 182, which then adds up to about $32,000. Why is a vehicle advertised like this? Numerically, $193 sounds a lot better than $32,000!
In business, whether you are setting up consumers with payment plans or buying and selling loan contracts, you need to calculate present values. As a consumer, you deal with present value calculations in a number of ways:
This section develops the present value formula for both ordinary annuities and annuities payable. As with future value calculations, these formulas adjust both simple and ordinary annuities as needed. From investments, we then extend the annuity calculation to loans as well.

The present value of any annuity is equal to the sum of all present values of all annuity payments when they run out to the beginning of the first payment interval. For example, let’s say you will receive an annual payment of $1,000 at the end of each payout interval for the next three years from an investment that yields 10% compounded annually. How much money should be in the annuity initially for this to happen? In this case, you have a simple ordinary annuity. The figure below illustrates the fundamental concept of time value of money and the calculation for moving all payments to the focal date at the beginning of the calendar.
Present Value Archives
Note that the three payments are worth up to your focal date, requiring an investment of $2,486.85 today. Conversely, what would happen to your calculations and calculations if those payments were made at the beginning of each payment interval? In this case, you have a simple annuity payable. The next figure shows your calculations and calculations.
Note that only two of the three payments need to be assessed by your focal date because the first payment is already due on the focal date. The total investment for an annuity payable is higher at $2,735.54 because the first payment is withdrawn immediately, so a smaller principal earns less interest than a normal annuity.
The next figure below contrasts the two types of annuities. Working from right to left on the timeline, the main difference is that there is less interest compounding to withdraw in an annuity payable. Its first section (from the right) has a zero balance, while the simple annuity has a balance that requires interest rebate. Note that if you take the annuity payable and take out another interest compound, you arrive at $2,735.54 (1 + 0.1) = $2,486.85, which is the present value of the corresponding simple annuity.
As with future value calculations, it is time consuming to calculate present values by manually taking each payment to its present value when there are more than a few payments. Similarly, annuity formulas allow you to run all the payments together in one calculation. The formulas for ordinary annuity and annuity payable are presented together.
Pv Calculator Factory Sale, 55% Off
Step 4: If (FV) = $0, then proceed to step 5. If there is a non-zero value for (FV), treat it as a single payment. Apply Formula 9.2 to determine (N) as this is not an annuity calculation. Using formula 9.3, move the future value to the beginning of the time segment, rearranged to (PV).
Step 5: Use Formula 11.1 to Calculate (N). Apply Formula 11.4 or Formula 11.5, depending on the type of annuity. If you calculated the present value in Step 4, add the present values from Steps 4 and 5 to get the total present value.
Calculation of interest amount. If you’re interested in knowing how much interest is removed in computing the present value, follow Formula 8.3, where (I = S – P =

Fv – pv). The current value ((PV)) is a solution to either Formula 11.4 or Formula 11.5. in (FV)
Annuity Calculator And Its Basics
This is expanded to include the sum of all future cash, so it is replaced with (N × PMT + FV). so you rewrite
Your BAII+ calculator. If the future value (FV) of a single payment is included in the present value calculation, this requires using two of the formula’s calculations.
And either Formula 11.4 or Formula 11.5. If you enter values that follow the cash flow sign convention for both (FV) and (PMT), the calculator performs these two calculations together.
For two identical investment annuities, will the present value of common annuity and annuity payable be the same or different?
Learn More Financial Calculator
They will be different. An annuity payable always has the greatest present value because it removes less interest compounding than an ordinary annuity.
Rodriguez plans to have an annual gross income of $50,000 at the end of each year when he retires at age 65. He plans to liquidate the account by age 78, which is the average life expectancy for a Canadian person. If the account earns 5.1% compounded annually, how much amount will be required in the account at the time of retirement?
Payments occur at the end of the payment interval, and the compounding period and the payout interval are the same. Therefore, it is a simple ordinary annuity. Calculate its value at the beginning, which is its current value, or (PV_).
(FV) = $0, (IY) = 5.1%, (CY) = 1, (PMT) = $50,000, (PY) = 1, year = 13
Timeline Use In Tvm Example Question
This figure shows how much the principal and interest pay. Rodriguez received his $466,863.69 . would be required
Net present value of annuity calculator, present value annuity payment calculator, net present value annuity calculator, present value annuity factor calculator, present value annuity formula calculator, calculator present value of annuity, present value ordinary annuity calculator, present value of annuity formula calculator, present value annuity due calculator, present value formula for annuity, annuity calculator present value, present value formula annuity
Post a Comment for "Annuity Calculator Present Value Formula"